Dye Packages / Rewinding
show general information-
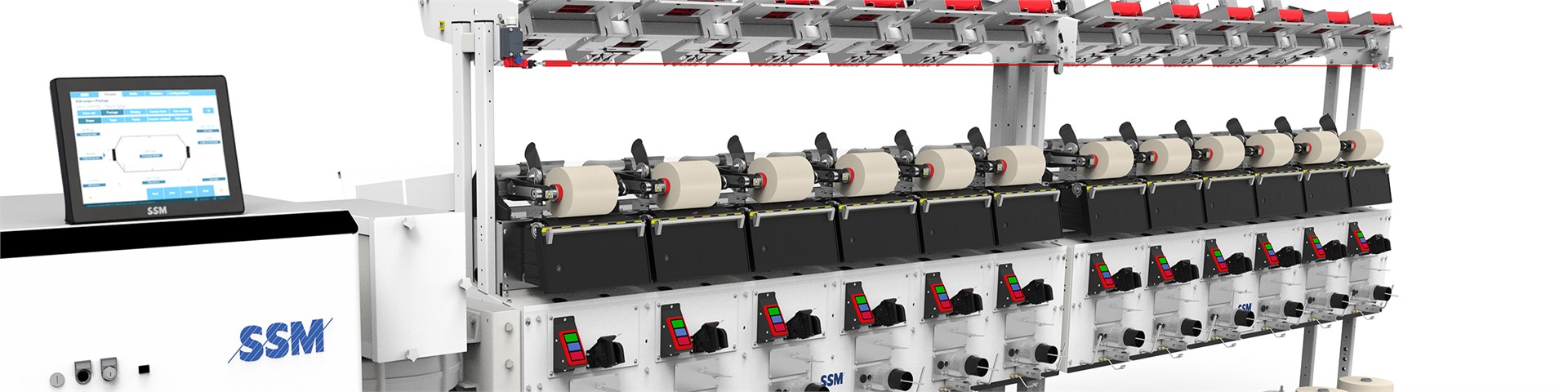
NEO-FW Precision package winder
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
COCotton
Natural fibre from the cotton plant which is spun into fine yarn.
-
PANPolyacryl
Synthetic fiber made from a polymer (Polyacrylonitrile, also known as Creslan61). PAN belongs to the family of acrylic resins. It is a hard, rigid thermoplastic material that is resistant to most solvents & chemicals, slow to burn and of low permeability to gases.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
The NEO-FW is a precision package winding machine for all kind of staple and textured filament yarns suitable for dye package winding, warping preparation and rewinding with or without lubrication or waxing. Equipped with the latest technology from SSM, it is the machine for made-to-measure cross-wound packages, which cuts down maintenance and service costs to a minimum.
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data NEO-FW
Type of winding
DIGICONE 2 or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 1500 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25 – 210 mm electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 250 mm
Package weight
up to 5 kg
Supply package diameter
up to 280 mm
Yarns
staple yarns and textured filament yarns
Yarn count range
Ne 3 – 80 (Nm 5 – 135 / 80 – 2 000 dtex) (other yarn counts on request)
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 5° 57' max. length 230 mm, min. base diameter 38 mm (smaller/larger diameters upon request)
Layout
single or double sided
N° of spindles per section
6 (single sided) and 12 (double sided)
N° of spindles min./max.
6 / 96 (single sided) and 12 / 120 (double sided, 2 × 60 back to back)
Gauge
360 mm
Drive
individual
Installed power
approximately 200 W per spindle
Power consumption
from 25 to 100 W per spindle (depending on winding parameters/options)
Blower (installed power)
up to 2 200 W (depending on blower type and manufacturer)
Compressed air
7 bar (only required for machines with automatic doffer / pneumatic bracket opener)
Downloads
-
SSM_NEO-FW_en.pdf
-
Cones
-
NEO-YW Precision package winder
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PPPolypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging and labeling, textiles (e.g., ropes, thermal underwear and carpets), stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes. An addition polymer made from the monomer propylene, it is rugged and unusually resistant to many chemical solvents, bases and acids.
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
-
PBTPolybutylene Terephthalate
PBT is similar to other thermoplasic polyesters. Compared to PET, PBT has a slightly lower strenth and rigidity, but a better impact resistance. The yarn has a natural stretch and can be incorporated into sports wear (most common found in swimwear).
-
SESilk
Natural protein fiber composed mainly of fibroin. Silk is produced by several insects, but generally only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing.
-
ARAramid
Aramid is the short term for aromatic polyamide. They are fibres, in which the chain molecules are highly oriented along the fibre axis, so the strength of the chemical bond can be exploited. The fibre is heat-resistant and of great strength. Aramid is used in materials for bulletproof vests and radial tires.
-
CVViscose
Viscose, formerly known as viscose rayon, is made by treating cellulose with caustic alkali solution and carbon disulphide. It is a soft fibre commonly used in dresses, linings, shirts, shorts, coats, jackets, and other outerwear.
Only a quick response to market trends in combination with high cost-efficiency enables yarn dyers to be successful with competitive advantages. The NEO-YW offers clear benefits to dye package winding and rewinding of filament yarns, with or without lubrication.
Key features:
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data NEO-YW
Type of winding
DIGICONE® 2 or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 2000 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25…270 mm electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 280 mm
Package weight
up to 8 kg
Supply package diameter
up to 300 mm
Yarns
textured or flat filaments, elastic yarns, silk, fine technical yarns, staple yarns
Yarn count range
– with digitens™ d or f : 10…2200 dtex / Nm 4.5...1000
– with digitens™ g : 10…3000 dtexTake-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 3° 30' for filament and up to 5° 57' for staple yarns max. length 290 mm, min. base diameter 46 mm, max. base diameter 95 mm
(smaller/larger dia. upon request)Layout
single or double sided
N° of spindles per section
6 (single sided) and 12 (double sided)
N° of spindles min. / max.
6 / 96 (single sided) and 12 / 120 (double sided, 2 × 60 back to back)
Gauge
360 mm
Drive
individual
Installed power
~250 W per spindle
Power consumption
~ 40…100 W per spindle (dep. on winding parameters/options)
Downloads
-
SSM_NEO-YW_en.pdf
-
Cones
-
NEO-BW Precision package winder
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
COCotton
Natural fibre from the cotton plant which is spun into fine yarn.
-
WOWool
Animal fibre; most commonly used to mean the yarn spun from the sheep.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
SESilk
Natural protein fiber composed mainly of fibroin. Silk is produced by several insects, but generally only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing.
-
ARAramid
Aramid is the short term for aromatic polyamide. They are fibres, in which the chain molecules are highly oriented along the fibre axis, so the strength of the chemical bond can be exploited. The fibre is heat-resistant and of great strength. Aramid is used in materials for bulletproof vests and radial tires.
-
CVViscose
Viscose, formerly known as viscose rayon, is made by treating cellulose with caustic alkali solution and carbon disulphide. It is a soft fibre commonly used in dresses, linings, shirts, shorts, coats, jackets, and other outerwear.
-
STSewing Thread
Sewing threads yarns are especially made to pass rapidly through a sewing machine. It is a fine cord of a fibrous material, made of two or more filaments twisted together. The yarn has to form efficient stitches without breaking or becoming distorted.
The SSM NEO-BW is a precision package winder for dye packages / rewinding and suitable for all kinds of spun yarn. The high productivity and reproducibility resulting in a minimum off-shade dyeing are the significant advantages for any dyer. The decisive success factor of the NEO-BW winder is its unique thread laying system by means of counter-rotating blades, which has established itself as the system, gentlest to the yarn. The rotating motion of the blades is practically wear-free and ensures highest production speeds at lowest possible operation costs.
Key features:
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data NEO-BW
Type of winding
DIGICONE® 2 or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 1600 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
cylindrical or conical
Traverse length
155 mm, mechanically adjustable ±5 mm
Take-up package diameter
up to 250 mm
Package weight
up to 5 kg
Supply package diameter
up to 300 mm
Yarns
all kinds of staple yarns
Count
Ne 1.2…120
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 4° 20' max. length 170 mm, min. base ø 43 mm (larger length/smaller dia. upon request)
Layout
single or double sided
N° of spindles per section
6 (single sided) and 12 (double sided)
N° of spindles min. / max.
6 / 96 (single sided) and 12 / 120 (double sided, 2 × 60 back to back)
Gauge
360 mm
Drive
individual
Installed power
~250 W per spindle
Power consumption
~ 40…100 W per spindle (dep. on winding parameters/options)
Blower (installed power)
up to 2200 W (dep. on blower type and manufacturer)
Downloads
-
SSM_NEO-BW_en.pdf
-
Cones
-
XENO-YW Precision package winder
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
COCotton
Natural fibre from the cotton plant which is spun into fine yarn.
-
WOWool
Animal fibre; most commonly used to mean the yarn spun from the sheep.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PPPolypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging and labeling, textiles (e.g., ropes, thermal underwear and carpets), stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes. An addition polymer made from the monomer propylene, it is rugged and unusually resistant to many chemical solvents, bases and acids.
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
-
PBTPolybutylene Terephthalate
PBT is similar to other thermoplasic polyesters. Compared to PET, PBT has a slightly lower strenth and rigidity, but a better impact resistance. The yarn has a natural stretch and can be incorporated into sports wear (most common found in swimwear).
-
SESilk
Natural protein fiber composed mainly of fibroin. Silk is produced by several insects, but generally only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing.
-
GFGlass fibre
Also called spun glass, is a material consisting of extremely fine filaments of glass that are combined in yarn and woven into fabrics. Used in making various products, such as yarns, fabrics, insulators, and structural objects or parts.
-
ARAramid
Aramid is the short term for aromatic polyamide. They are fibres, in which the chain molecules are highly oriented along the fibre axis, so the strength of the chemical bond can be exploited. The fibre is heat-resistant and of great strength. Aramid is used in materials for bulletproof vests and radial tires.
-
ELElastan
Elastane or Spandex is a polyurethane-polyurea copolymer. This synthetic fibre can be stretched from four to seven times their length, reverting to their original length when the tension is relaxed. Used for all areas where a high degree of permanent elasticity is required: hosiery, underwear, sportswear, and in woven and knitted fabrics.
-
CVViscose
Viscose, formerly known as viscose rayon, is made by treating cellulose with caustic alkali solution and carbon disulphide. It is a soft fibre commonly used in dresses, linings, shirts, shorts, coats, jackets, and other outerwear.
-
STSewing Thread
Sewing threads yarns are especially made to pass rapidly through a sewing machine. It is a fine cord of a fibrous material, made of two or more filaments twisted together. The yarn has to form efficient stitches without breaking or becoming distorted.
-
TYTechnical Yarns
The yarns are used for technical textile products, manufactured for non-aesthetic purposes, where function (rigidity, strength, dimension stability, design flexibility and economic viability) is the primary criterion.
SSM XENO - the new modular winding machine platform, available with all three leading SSM winding technologies.
The XENO-YW is a precision winding machine for all kind of staple and filament yarns suitable for dye package winding, warping preparation and rewinding with or without lubrication or waxing.The key features are:
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data XENO-YW
Type of winding
DIGICONE® 2 or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 2000-2500 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25...270 mm electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 300 mm
Package weight
up to 10 kg
Supply package diameter
up to 320 mm
Yarns
staple yarns, monofilament, textured filaments, flat or twisted filament yarns, medium technical yarns
Count
Ne 1.5...240 / 10...4000 dtex
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 5° 57’
max. length 290 mm, min. base diameter 38 mm (smaller diameters upon request)
max. diameter with automatic doffer: inner 87 mm, outer 96 mmLayout
single or double sided
N° of spindles per section
5 (single sided) or 10 (double sided)
N° of spindles min. / max.
5 / 80 (single sided) and 10 / 80 (2 x 40 double sided, back to back)
Gauge
440 mm
Drive
Individual
Installed power
~250 W per spindle
Power consumption
~18...110 W per spindle (depending on winding parameters / options)
Blower (installed power)
up to 2200 W (depending on blower type and manufacturer)
Compressed air
6 bar (only required for machines with automatic doffer / pneumatic bracket opener)
Downloads
-
SSM_XENO-YW_en.pdf
-
Cones
-
XENO-YW precitens™ Dye Packages / Rewinding
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
Muffs (Hanks)
for the dyeing process of high elastic filament yarns - depending on the machine execution different types of muffs (hanks) could be prepared
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
DTYDrawn Textured Yarn
Made from Polyester POY by simultaneously twisting & drawing. DTY yarn is mainly used in weaving and knitting.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
Due to the unique machine design, SSM can offer a versatile machine for both, muff preparation (cone to muff) as well as unrolling of the muffs after dyeing (muff to cone). For the customer this results in higher flexibility, lower investment costs and last but not least, more profit.
show more textshow less text
Muff dyeing
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data XENO-YW precitens™
Type of winding
DIGICONE® 2 or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 2500 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25...270 mm electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 300 mm
Package weight
up to 10 kg
Unwinding tension
2– 40 cN
Supply package
- traverse length
- weight
- max. diameter
- inner tube diameter
- tube length
up to 250 mm
up to 3.0 kg (incl. tube)
up to 370 mm
44…72 mm
up to 290 mmHank
- width
- weight
- diameter
up to 310 mm
up to 3.0 kg (incl. hank)
up to 370 mmYarns
high elastic filament yarns (PA or PES DTY)
Count
22…800 dtex
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 3° 30'
max. length 290 mm, min. base diameter 43 mm (smaller dia. upon request)
max. diameter with automatic doffer: inner 87 mm, outer 96 mmLayout
single-sided
N° of spindles per section
5
N° of spindles min. / max.
5 / 60
Gauge
440 mm
Drive
individual
Installed power
~450 W per spindle
Power consumption
~100...220 W per spindle (dep. on winding parameters /options)
Compressed air
6 bar (only required for machines with automatic doffer)
Downloads
-
SSM_XENO-YW-precitens_gb_2020.pdf
-
Cones
-
XENO-PB Precision package winder
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
COCotton
Natural fibre from the cotton plant which is spun into fine yarn.
-
WOWool
Animal fibre; most commonly used to mean the yarn spun from the sheep.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
SESilk
Natural protein fiber composed mainly of fibroin. Silk is produced by several insects, but generally only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing.
-
CVViscose
Viscose, formerly known as viscose rayon, is made by treating cellulose with caustic alkali solution and carbon disulphide. It is a soft fibre commonly used in dresses, linings, shirts, shorts, coats, jackets, and other outerwear.
-
STSewing Thread
Sewing threads yarns are especially made to pass rapidly through a sewing machine. It is a fine cord of a fibrous material, made of two or more filaments twisted together. The yarn has to form efficient stitches without breaking or becoming distorted.
The SSM XENO-PB, with its innovative powerblade™ yarn laying system, is a precision winding machine to produce perfectly wound packages for all kind of staple yarns. It is the first winding machine worldwide with counter-rotating blade traverse system, on which the shape of the dye package can be optimally adapted in means of traverse variation (for soft edges) and package shape (tapered or round edges) for dye package dyeing.
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data XENO-PB
Type of winding
DIGICONE® 2 or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 2200 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
symmetrical, freely programmable
Traverse length
100...163 mm, electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 250 mm (up to 230 mm with doffer)
Package weight
up to 8 kg
Supply package diameter
up to 320 mm
Yarns
staple yarns (filament yarns upon request)
Count
Ne 1…120
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 5° 57'
max. length 235 mm, min. base diameter 38 mm (smaller dia. upon request)
max. diameter with automatic doffer: inner 87 mm, outer 96 mmLayout
single or double-sided
N° of spindles per section
6 (single-sided) or 12 (double-sided)
N° of spindles min. / max.
6 / 96 (single-sided) and 12 / 120 (2 × 60 double-sided, back to back)
Gauge
367 mm
Drive
Individual
Installed power
~ 360 W per spindle
Power consumption
~45…100 W per spindle (dep. on winding parameters /options)
Blower (installed power)
up to 2200 W (dep. on blower type and manufacturer)
Compressed air
6 bar (only required for machines with automatic doffer /pneumatic bracket opener)
Downloads
-
SSM_XENO-PB_gb.pdf
-
Cones
-
DURO-TW precision package winder for technical yarns
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
COCotton
Natural fibre from the cotton plant which is spun into fine yarn.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PPPolypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging and labeling, textiles (e.g., ropes, thermal underwear and carpets), stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes. An addition polymer made from the monomer propylene, it is rugged and unusually resistant to many chemical solvents, bases and acids.
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
-
PBTPolybutylene Terephthalate
PBT is similar to other thermoplasic polyesters. Compared to PET, PBT has a slightly lower strenth and rigidity, but a better impact resistance. The yarn has a natural stretch and can be incorporated into sports wear (most common found in swimwear).
-
GFGlass fibre
Also called spun glass, is a material consisting of extremely fine filaments of glass that are combined in yarn and woven into fabrics. Used in making various products, such as yarns, fabrics, insulators, and structural objects or parts.
-
ARAramid
Aramid is the short term for aromatic polyamide. They are fibres, in which the chain molecules are highly oriented along the fibre axis, so the strength of the chemical bond can be exploited. The fibre is heat-resistant and of great strength. Aramid is used in materials for bulletproof vests and radial tires.
-
TYTechnical Yarns
The yarns are used for technical textile products, manufactured for non-aesthetic purposes, where function (rigidity, strength, dimension stability, design flexibility and economic viability) is the primary criterion.
The SSM DURO-TW precision winder for coarse technical yarns up to 50000 dtex offers a new level of flexibility and winding quality in one machine; thereby ensuring the fulfillment of all customer requirements.
show more textshow less text
The key features are:
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data DURO-TW
Types of winding
DIGICONE® or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 1500 m/min (winding speed depending on winding parameters, yarn quality and supply packages)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25...320 mm
Take-up package diameter
up to 320 mm
Package weight
up to 24 kg
Supply package diameter / height
up to 380 mm / 600 mm
Yarns
all staples and filament yarns
Count
up to 50000 dtex (up to Ne 0.12 / up to Nm 0.2) (coarser upon request)
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 3° 30'
max. length 355 mm, min. base diameter 38 mmLayout
single sided
N° of spindles per section
2
N° of spindles min. / max.
2 / 40
Gauge
550 mm
Drive
individual
Power consumption
150...500 W (depending on winding parameters)
Compressed air
6 bar
Downloads
-
SSM_DURO-TW_gb_2020.pdf
-
Cones
-
PWX-CTM Cone-to-muff winder
-
Muffs (Hanks)
for the dyeing process of high elastic filament yarns - depending on the machine execution different types of muffs (hanks) could be prepared
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
DTYDrawn Textured Yarn
Made from Polyester POY by simultaneously twisting & drawing. DTY yarn is mainly used in weaving and knitting.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
To maintain a high residual elasticity of elastic Polyamide (PA) and Polyester (PES) draw textured yarns (DTY) after dyeing, the muff dyeing process with integrated SSM leading yarn winding technology is the best solution.
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical Data PWX-CTM
Type of winding
SSM Precision winding
Mechanical speed
up to 1500 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25...270 mm electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 520 mm (Expander 200…350 or 250...500 mm)
Package weight
up to 3 kg
Winding tension
2-40 cN
Supply package diameter
up to 400mm
Yarns
All elastic filament yarns (PA or PES DTY), CCY, corespun
Count
10…1200 dtex
Layout
single-sided
N° of spindles per section
4
N° of spindles min. / max.
4 / 48
Gauge
550 mm
Drive
individual
Installed power
~250 W per spindle
Power consumption
~90...150 W per spindle (dep. on winding parameters /options)
Downloads
-
SSM_PWX-CTM_gb.pdf
-
Muffs (Hanks)
-
PWX-MTC Muff-to-cone winder
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
DTYDrawn Textured Yarn
Made from Polyester POY by simultaneously twisting & drawing. DTY yarn is mainly used in weaving and knitting.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
The SSM PWX-MTC is the ideal machine for rewinding of high elastic Polyamide (PA) and Polyester (PES) draw textured yarns (DTY) after dyeing. The online tension controlled, positively driven unrolling system precitens™ offers the highest flexibility and productivity.
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data PWX-MTC
Type of winding
DIGICONE® or precision
Mechanical speed
up to 1200 m/min (process speed depending on process parameters)
Package shape
freely programmable
Traverse length
25...270 mm electronically adjustable
Take-up package diameter
up to 280 mm
Package weight
up to 8 kg
Unwinding tension
2-40 cN
Supply package
- traverse length
- weight
- max. diameter
- inner tube diameter
- tube length
up to 250 mm
up to 3.0 kg (incl. tube)
up to 370 mm
44...72 mm
up to 290 mmMuff
- width
- weight
- diameter
up to 250 mm
up to 3.0 kg (incl. muff)
up to 360 mm (inside) / up to 400 mm (outside)Yarns
All elastic filament yarns (PA or PES DTY), CCY, corespun
Count
10…1200 dtex
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 3° 30'
max. length 290 mm, min. base diameter 46 mm (other dia. upon request)Layout
single-sided
N° of spindles per section
5
N° of spindles min. / max.
5 / 60
Gauge
450 mm
Drive
individual
Installed power
~450 W per spindle
Power consumption
~100...220 W per spindle (dep. on winding parameters /options)
Downloads
-
SSM_PWX-MTC_gb_2020.pdf
-
Cones
-
MED-1 Muff expanding device
-
Muffs (Hanks)
for the dyeing process of high elastic filament yarns - depending on the machine execution different types of muffs (hanks) could be prepared
-
FilamentYarnFilament Yarn
Synthetic yarn composed of one or more filaments that run the whole length of the yarn. Yarns of one filament are referred to as mono-filament; yarns of several filaments as multi-filament.
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
DTYDrawn Textured Yarn
Made from Polyester POY by simultaneously twisting & drawing. DTY yarn is mainly used in weaving and knitting.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
PAPolyamid
Also known as Nylon. PA consists of chemical fibres and are obtained from synthetic polymers. Polyamid is very resistant and tear proof as well as elastic, stretchable and takes just a little moisture up. In addition it is extensively crease-resistant and drip-dry.
With the new SSM Muff Expander, dyed muffs made of elastic yarn are opened gently and consistently in order to be positioned easily and reliably on the muff unwinding swift or expander.
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data MED-1
Opening/closing speed
adjustable
Diameter expanding arms
minimum 70mm
maximum in 3 versions available:
up to 245, 325 or 360 mmWorking material
high elastic yarns
Installed power
not requested
Compressed air
6 bar
Downloads
-
SSM_MED-1_gb_2020.pdf
-
Muffs (Hanks)
-
CWX-W Random winding machine
-
Cones
for a conical package shape
-
Tubes
or cops are the most flexible base for a wide range of package shapes (e.g.: cylindrical - no taper / biconical - double taper / single taper / bottle shape), depending on the winding unit (type of winding)
-
SpunYarnSpun yarn
Textile yarn spun and twisted from staple length fiber, either natural or synthetic.
-
COCotton
Natural fibre from the cotton plant which is spun into fine yarn.
-
PET / PESPolyester
Synthetic fiber made from a thermoplastic polymer that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene succinate (PES) with a melting point from 103 – 106°C
-
SESilk
Natural protein fiber composed mainly of fibroin. Silk is produced by several insects, but generally only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing.
-
CVViscose
Viscose, formerly known as viscose rayon, is made by treating cellulose with caustic alkali solution and carbon disulphide. It is a soft fibre commonly used in dresses, linings, shirts, shorts, coats, jackets, and other outerwear.
The CWX-W, the new energy efficient drum winder is a rewinding machine for cones used in the weaving, warp knitting and circular knitting process.
show more textshow less text
show more factsshow less factsTechnical data CWX-W
Type of winding
ClassicWind™ drum winding, random
Mechanical speed
up to 1500 m/min (process speed depending on quality of yarn and feed packages)
Package shape
cylindrical or conical up to 5° 57'
Traverse length
152 mm (6")
Take-up package diameter
– cylindrical: up to 270 mm
– conical > 3° 30': up to 275 mmPackage weight
up to 3 kg
Supply package diameter
up to 240 mm, other dimensions on request
Yarns
staple yarns
Count
Ne 3...120 (Nm 5...200), other yarn counts on request
Take-up tubes
cylindrical or cones up to 5° 57', length 165…175 mm
diameter: cylindrical min. 38 mm / conical base diameter min. 38 mm, top inner diameter min. 18 mm (smaller diameter upon request)Layout
double sided machine
N° of spindles per section
16
N° of spindles min. / max.
16 / 128 (8 double-sided sections)
Gauge
270 mm
Drive
individual, all settings adjustable per spindle
Installed power
~125 W per spindle
Power consumption
35…75 W per spindle (dep. on speed, yarn count, yarn tension, anti patterning)
Blower
up to 2200 W depending on blower type and manufacturer
Downloads
-
SSM_CWX-W_gb_2020.pdf
-
Cones
 SSM - Leading Swiss technology for yarn processing and winding
SSM - Leading Swiss technology for yarn processing and winding